What makes a Taylor Swift song popular? Several answers could come to mind: the poetic beauty of her songwriting, the deft skill of her producers, the power of the bridge, her emotive vocal performance. Certainly, these matter. But each of these answers is also limited because each focuses on the characteristics of one song in isolation. My semantic analysis of Taylor Swift’s lyrics suggests a different kind of answer: A Taylor Swift song’s popularity arises from its connection to other Taylor Swift songs.
I’ll discuss the data supporting that claim in a moment, but I want to do so by way of something I’ve never written about here: My own story of how I became a Swiftie.
My journey into the Taylorverse
In my childhood, I listened to a number of female country artists, and in my mid-twenties, I enjoyed singers that were, at the time, also catering to a similar audience as Taylor Swift (Hilary Duff, Aly & AJ, Miley Cyrus). That was good preparation, and although I can’t pinpoint the first time I heard Taylor, it was probably on the radio or on Yahoo’s music streaming service.
I do know that, in June 2009, I was driving down New Hampshire St. in Lawrence, Kansas. I was on a business trip as a young assistant professor, attending a weeklong seminar on advanced social science statistics. “Love Story” came on the radio. It wasn’t the first time I’d heard the song, but I remember thinking to myself, “Yeah, this is good stuff—I could be a Taylor Swift fan.” That’s the point when I’d say my journey into the Taylorverse began.
Later, I bought a used copy of Fearless, then Speak Now, then debut, and then I bought Red when it was a new release. As I listened, I began to appreciate that Taylor wasn’t writing just songs; she was writing albums. That’s maybe not the case with debut, which feels like a (very good) group of songs, but in Fearless and especially Speak Now, it was becoming evident that her albums were cohesive artistic statements as a whole. Fearless celebrates the closeness and challenges of teenage girls’ relationships; Speak Now is about finding one’s voice in the journey of growing up. By Red, a tour de force of romantic passion and heartbreak, the deeply thematic nature of her albums was undeniable. Yes, the songs matter; but the song’s context, what we would now call its era, deeply shapes her work.
Then, moving into 1989 and Reputation and beyond, I realized the connections weren’t only within albums, but between them. “A circus ain’t a love story” ties Reputation to Fearless. “Blank Space” wryly caricatures her media persona in her early albums. “I once believed love would be burning red,” she sings in Lover’s “Daylight.” Then “Bad Blood” is playing in a cab on Folklore, and then “You’re on Your Own, Kid” summarizes her entire career… you get the idea, and there are so many other examples.
To call these lyrical connections “Easter eggs” is a bit too trite. Perhaps these connections are more than a bonus for astute fans, but rather part of the fabric—the ‘invisible string,’ if you will—that unites the art. That’s what my research tried to examine quantitatively.
Which Taylor Swift songs have the most word overlap with other songs?
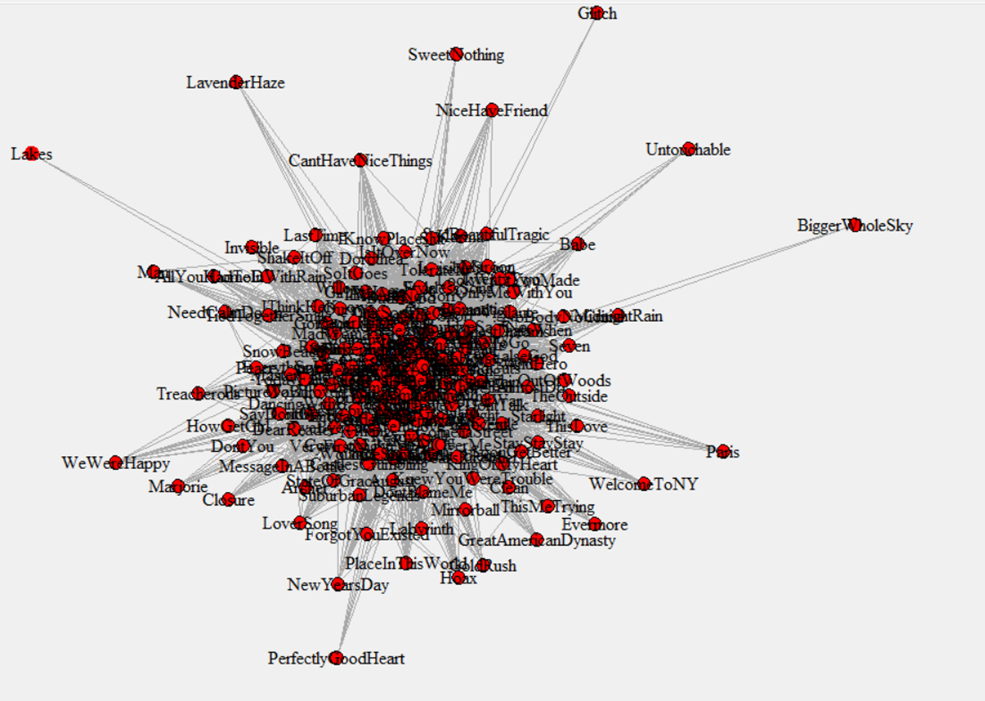
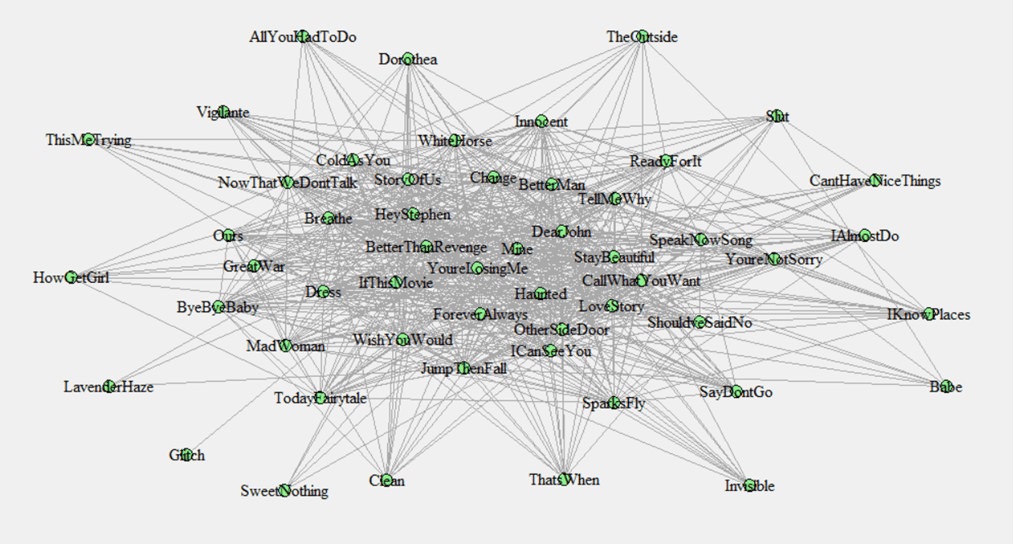
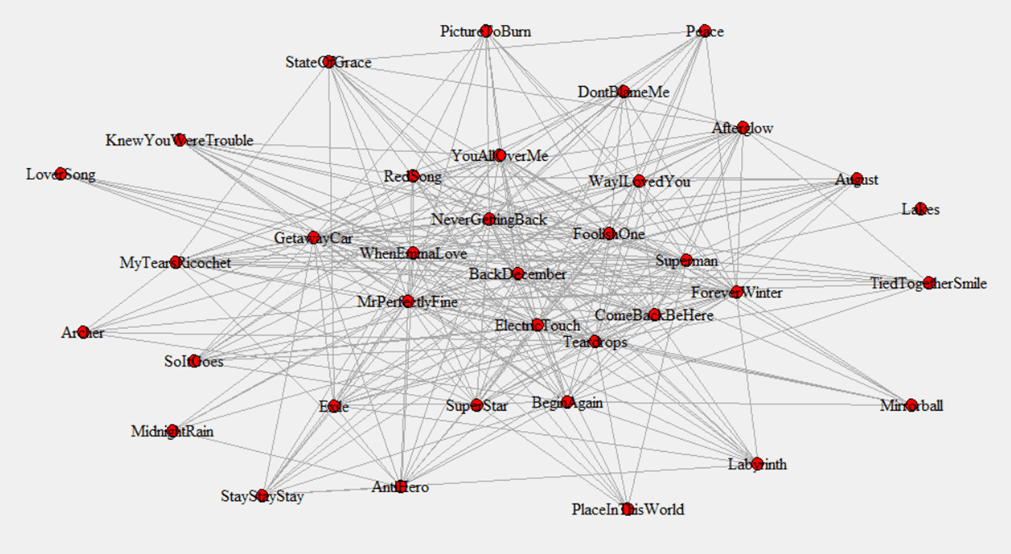
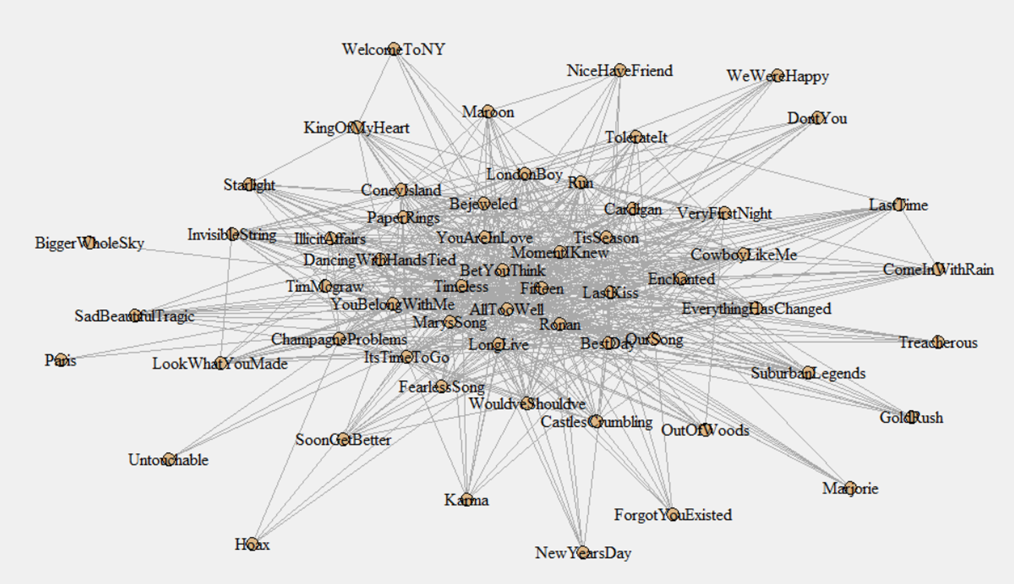
In the previous post, I described how 13 shared words is the minimum threshold where it made sense to treat two Taylor Swift songs as connected. Of course, the more words in common, the stronger the connection. We can use that information to create a map of the links between songs (again, discussed in the last post; also, see here for a list of all songs ranked by centrality, including TTPD).
Once we have that map, we can calculate something called a song’s centrality. (For those interested in the technical details, I used eigenvector centrality in the analysis.) Some songs are highly connected to other songs; their centrality is high. Here are the 15 songs that are most highly connected to other songs, in ascending order of centrality:
- #15: “When Emma Falls in Love”
- #14: “You’re On Your Own, Kid”
- #13: “Dear John”
- #12: “Foolish One”
- #11: “You’re Losing Me”
- #10: “Better Than Revenge”
- #9: “Betty”
- #8: “Mine”
- #7: “I Bet You Think About Me”
- #6: “Hits Different”
- #5: “Blank Space”
- #4: “Mr. Perfectly Fine”
- #3: “Timeless”
- #2: “All Too Well” [original; I didn’t include 10-minute in the analysis]
- #1: “Fifteen”
You might already have a rough sense of what’s going on here… not all of these are stone-cold Taylor classics, but there’s a decent number of singles, big hits, and fan favorites among the most central songs.
Other songs are on the fringe of the map, with few connections to other songs; their centrality is low. Here are the songs with the lowest centrality:
- #186: “Evermore”
- #187: “This is Why We Can’t Have Nice Things”
- #188: “The Man”
- #189: “Welcome to New York”
- #190: “A Perfectly Good Heart”
- #191: “We Were Happy”
- #192: “Paris”
- #193: “It’s Nice to Have a Friend”
- #194: “Sweet Nothing”
- #195: “Untouchable”
- #196: “Lavender Haze”
- #197: “Glitch”
- #198: “Bigger Than the Whole Sky”
- #199: “The Lakes”
- #200: “Epiphany” (a song so disconnected it was excluded from all further analysis)
Now, I imagine every Swiftie has a song or two (or more) they like among these least central songs (I’m partial to “Evermore” and “The Lakes,” myself). But, aside from “The Man,” it’s hard to argue any of these are among her most beloved songs. Also, I was curious, so just now I checked Spotify stream counts again. As I write this, four of these songs (“A Perfectly Good Heart,” “It’s Nice to Have a Friend,” “Epiphany,” and “Glitch”) have the lowest number of streams on their respective albums (Taylor Swift, Lover, Folklore, and Midnights).
Song centrality predicts song popularity
So, just by eyeballing the list of central and not-central songs, we might have a sense that song centrality is positively associated (correlated) with song popularity. In other words, the more central the song, the more popular it is. But, as I tell my students, we can’t conduct statistical tests with our eyeballs. We need to conduct statistical tests with… um… statistics.
But to get statistics, we need to know how to measure what we want to measure. We’ve already measured song centrality. But what about song popularity? How should we measure something as debatable as that?
Because song popularity is somewhat vague, I chose to measure it three ways that combine into a fourth:
- Spotify stream count. One day, in a meeting that was kind of boring, I manually wrote down every Spotify stream count for all of the songs in a spreadsheet. Time well spent, for sure.
- Expert ranking. Yes, I’ve ranked the songs myself, but that would be a bit of a conflict of interest to include my own rankings in the analysis, wouldn’t it? So, I used an aggregation of Rob Sheffield’s rankings at Rolling Stone and Nate Jones at Vulture.
- Twitter/X conversation. Using the resources available in our Schieffer Media Insights Lab at TCU, I obtained 17,092 unique tweets, posted between February 1, 2022 and February 15, 2024, about the poster’s favorite Taylor Swift songs. The paper contains more detail about how this data was processed to get a measure of how frequently each song was mentioned.
- Overall popularity: We can combine the three measures together into an overall index of the song’s popularity.
Now, you might already see some problems with this approach, particularly for Twitter/X conversation (I’ll just call it Twitter from now on, to keep it simple, and sorry, that’s just a better brand name than X). Taylor released some albums during that time window (Midnights, Speak Now TV, and 1989 TV), so we might expect those songs to show up more in the Twitter data. Same for any song performed in the North American Eras Tour, which was vibrant during that time. Even Spotify data isn’t a perfect indicator of song popularity, because Taylor’s first three albums were released before Spotify was available in the United States, and she then removed her music from Spotify during the 1989 era. Even critics’ evaluations might be subject to these influences.
This is a common occurrence in social science: We want to look at the association between two things (in this case, song centrality and song popularity), but confounding variables get in the way. We can solve that by controlling for those confounding variables. And, doing that actually told an interesting story about some other factors that shape popularity:
- Album: Critics prefer the later albums, and later albums are more popular overall.
- Track: Tracks earlier on an album tend to be preferred across the board: They are streamed more, talked about on Twitter more, critics like them more, and they are more popular overall. Said differently, later tracks on an album are less popular (ever push “play” on an album and stop halfway through, maybe because you’re bored or the car ride ends?).
- Release date: Later releases have more streams, and songs released in the 2-year window are talked about more on Twitter.
- Eras setlist: Songs on the Eras Tour setlist were more popular on Twitter and among critics, as well as overall.
Finally, we can address the main question (“Question…?” 😉): Are songs with greater word overlap with other songs (i.e., with higher song centrality) more popular? And the answer is, yes, they are! Songs with higher centrality are more popular with critics, more popular on Twitter, almost more popular on streams (barely missed the threshold of statistical significance), and more popular overall.
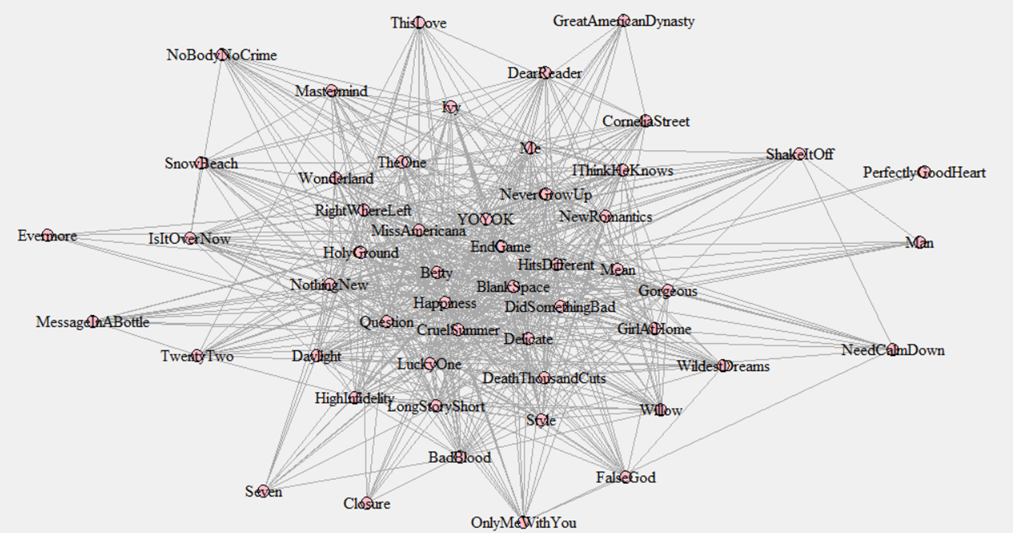
This is hard to visualize, in part because Taylor has so many songs. (And we Swifties are grateful for that!) Here’s a plot I used to demonstrate this to an audience recently, using a smaller selection of songs. Larger circles indicate more popular songs, with thicker lines meaning that the song shares more words in common. And, songs toward the center of the graph are more central, with those on the outside more peripheral. It seems that there is a knot of very popular songs at the center with lots of word overlap with other songs (“Cruel Summer,” “All Too Well,” “Long Live,” “Blank Space,” “Getaway Car”), while songs on the periphery are less popular.

Summary and Conclusion
So, then, yes: These results are consistent with the idea that the connection between Taylor’s songs is part of the appeal of her art. A caution, though, that we social scientists like to give: Just because two things are associated does not necessarily mean that one causes the other. Yes, it could be that audiences gravitate toward cohesive albums that connect to other parts of an artist’s work. Or, it could be that Taylor sees which songs audiences like, and makes those songs central by writing songs more like them.
My guess as to what’s going is, well, “both of these things can be true” (“Happiness”). Any artist’s popularity is crafted together with the fans who support them, something that Taylor has emphasized throughout her career. This again calls back to connections: It is the connections between the songs, as well as the artist and her fans, that animates her art and fuels its success.
In summary, my semantic network analysis found that:
- We can map Taylor Swift songs based on their word overlap with other Swift songs.
- The songs cluster into four core stories of (1) Villains and Heroes, (2) Longing and Regret, (3) Extraordinary Meaning in the Ordinary, and (4) Empowered Voice.
- Taken all together, these four core stories form an overarching narrative of a woman moving from victim to voice, a journey of finding feminine meaning and worth in a masculine world that devalues such things.
- Songs with high centrality (i.e., word overlap) tend to be more popular than songs with low centrality.
- This is consistent with the claim that the discography forms a “Taylorverse” of interconnected meanings, and these connections are part of the appeal of her music.